Current and Historical Weather Patterns: Texas Weather
Texas’s climate is characterized by hot, humid summers and mild winters. The state experiences a wide range of weather conditions, from severe thunderstorms and tornadoes to droughts and floods.
Current Weather Conditions
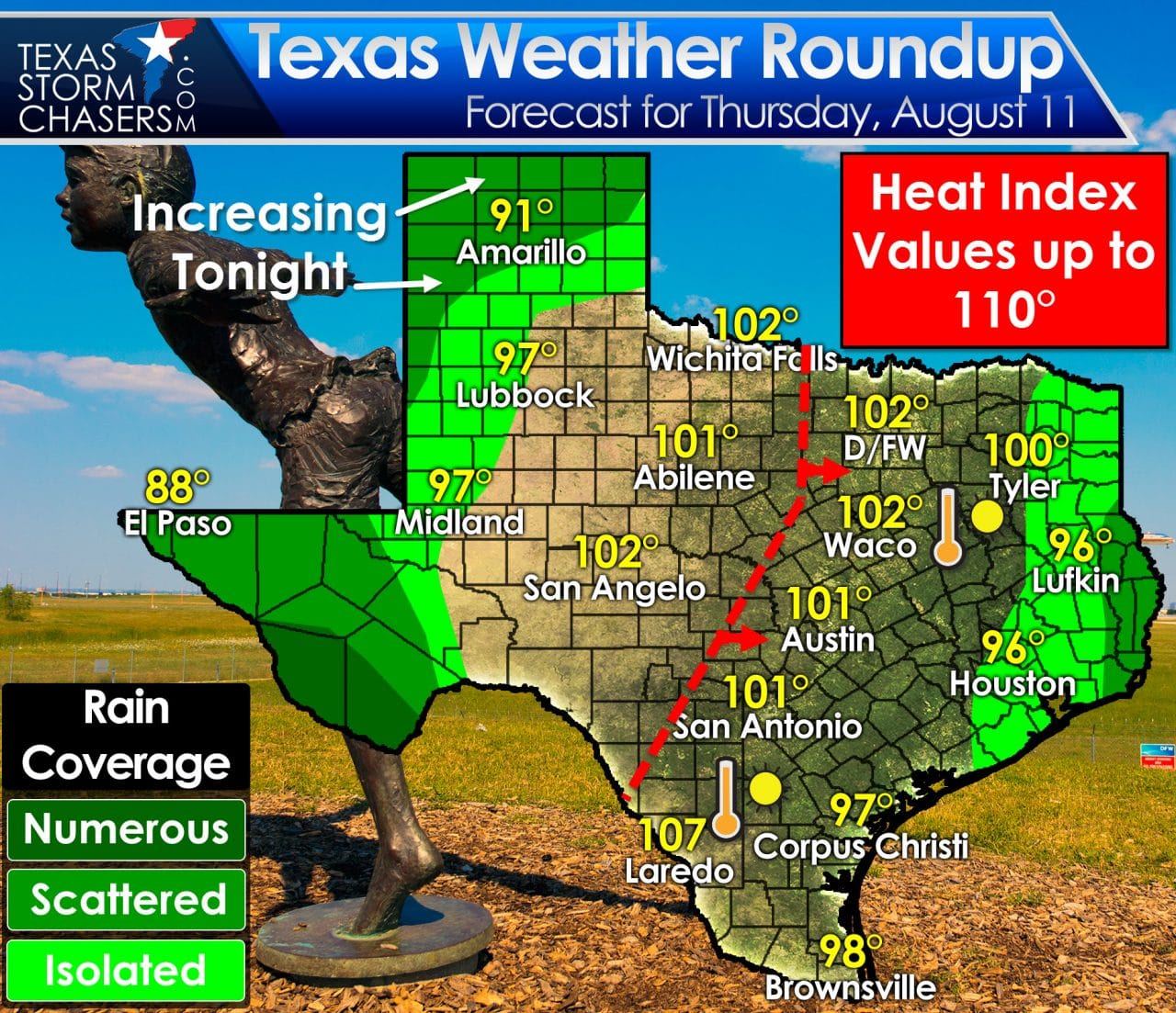
As of today, [date], the weather in Texas is mostly sunny with temperatures in the mid-80s. Humidity is moderate, and the wind is blowing at 10-15 mph. There is a slight chance of rain in the afternoon.
Historical Weather Patterns
Texas has a long history of extreme weather events. The state has been hit by numerous hurricanes, tornadoes, and floods. In 1900, the Galveston hurricane killed more than 8,000 people. In 1999, Hurricane Floyd caused widespread flooding in Texas.
The following table compares current and historical weather data for major cities in Texas:
| City | Average Temperature (°F) | Average Rainfall (inches) |
|—|—|—|
| Austin | 68.2 | 32.1 |
| Dallas | 66.9 | 38.1 |
| Houston | 71.6 | 50.5 |
| San Antonio | 69.6 | 29.8 |
As you can see, the weather in Texas can vary significantly from city to city. However, the state as a whole experiences a humid subtropical climate with hot summers and mild winters.
Climate and Geography

Texas weather – Texas, known for its vast and diverse landscapes, encompasses various climate zones and geographical features that shape its unique weather patterns.
The Gulf of Mexico, located on the state’s southeastern border, significantly influences the climate of the coastal regions. The Rocky Mountains, situated to the west, create a barrier against Pacific air masses, contributing to the state’s generally arid climate. The Edwards Plateau, a vast limestone plateau in central Texas, plays a role in shaping local weather patterns.
Climate Zones, Texas weather
Texas experiences a wide range of climate zones, each with distinct characteristics:
- Humid Subtropical: This zone covers the eastern and southeastern parts of Texas, characterized by hot, humid summers and mild winters. It receives ample rainfall throughout the year.
- Subtropical Desert: Found in the western part of Texas, this zone experiences extreme temperature variations, with scorching summers and cold winters. Precipitation is scarce.
- Semi-Arid: The central and northern regions of Texas fall under this zone, featuring hot summers and cold winters. Precipitation is moderate.
- Continental: This zone is located in the northernmost part of Texas, experiencing warm summers and cold, snowy winters. Precipitation is relatively consistent throughout the year.
Geographical Features
The geographical features of Texas play a crucial role in influencing its weather patterns:
- Gulf of Mexico: The Gulf’s warm waters contribute to the humid subtropical climate of the coastal regions. It also provides moisture for rainfall and supports frequent thunderstorms.
- Rocky Mountains: The Rocky Mountains act as a barrier, blocking Pacific air masses from entering Texas. This contributes to the state’s generally arid climate.
- Edwards Plateau: This limestone plateau affects local weather patterns by absorbing heat during the day and releasing it at night, creating temperature inversions.
The interplay between these climate zones and geographical features results in the diverse and dynamic weather patterns observed across Texas.
Texas weather is known for its unpredictability, with scorching summers and mild winters. But what about tropical storms? Hurricane Beryl is currently making its way towards the Gulf of Mexico, and many are wondering when it will hit Texas. To stay up-to-date on the latest forecasts and track the storm’s path, visit when will beryl hit texas.
With its real-time updates and interactive maps, you’ll be able to stay informed and make informed decisions about your safety.
The capricious weather of Texas, with its sweltering summers and frigid winters, poses a unique challenge for its power grid. To address this, the state has formed a partnership with neighboring New Mexico, known as the Texas-New Mexico Power Partnership.
This collaboration allows for the sharing of energy resources, ensuring a more stable and reliable power supply for both states. Despite these measures, the unpredictable nature of Texas weather remains a constant reminder of the importance of robust infrastructure and sustainable energy practices.